Probabilistic modeling of mechanical properties in thymol-loaded gelatin films for nano wound dressing applications
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.61882/jcc.6.3.6Abstract
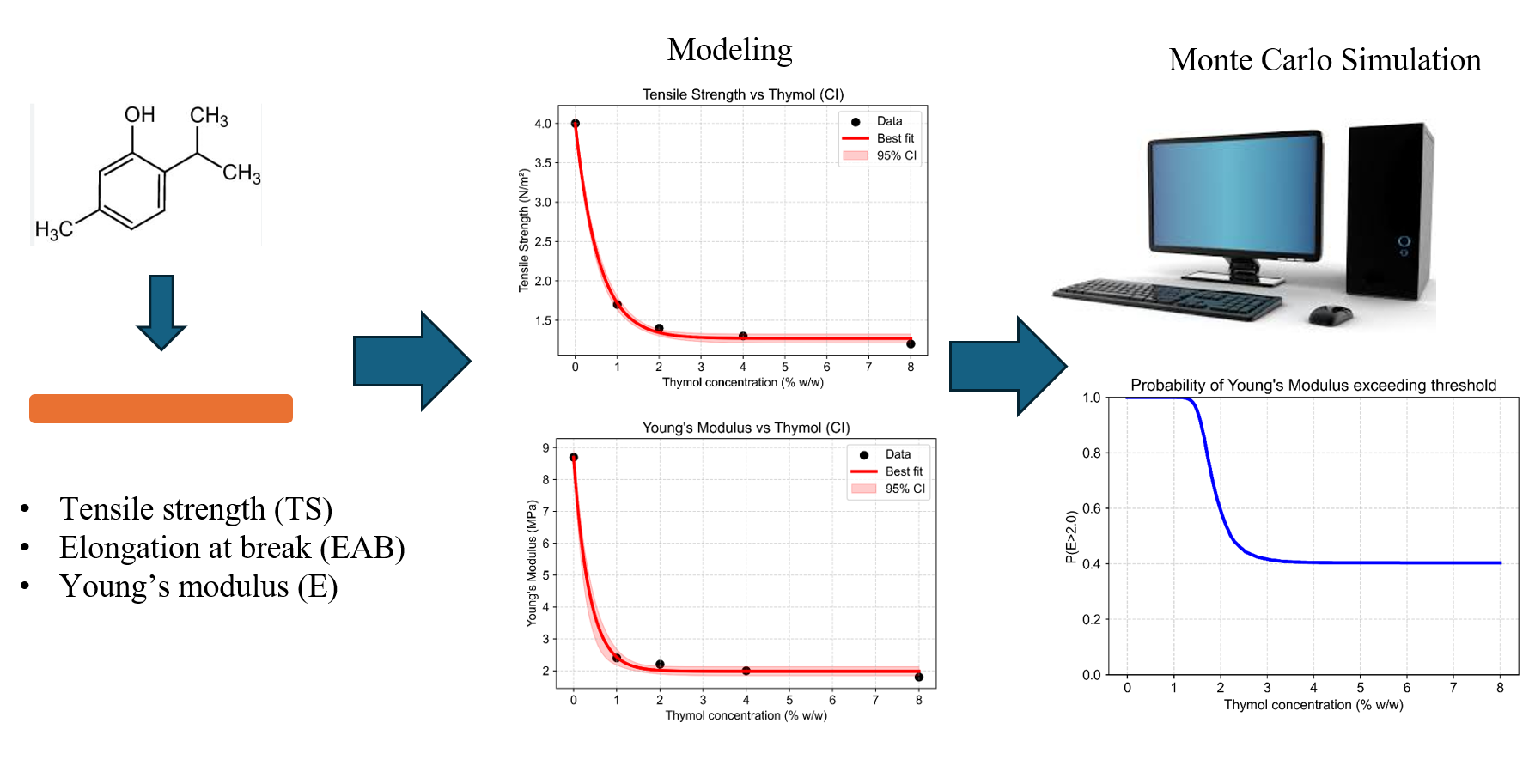
Gelatin-based films modified to contain thymol represent an exciting new bioactive material class designed for advanced wound dressing applications. Thymol provides favorable antioxidant and antimicrobial activity; however, we need a quantitative understanding of its effect on the ability of gelatin films to bear a load, which will enable the rational design of these products. The goal of this work was to develop a physics-informed probabilistic modeling framework to predict and analyze the mechanical properties (tensile strength (TS), elongation at break (EAB), and Young’s modulus (E)) of thymol-loaded gelatin films as a function of thymol concentration (0–8% w/w), using published experimental data. We fit exponential decay and saturating functions to capture the concentration dependent trends, and used a Monte Carlo simulation (5,000 trials) to quantify the uncertainty in the parameters and to estimate the probability of meeting functional mechanical thresholds (TS > 1.5 N/m², EAB > 155%, E > 2.0 MPa). Our work shows a fundamental trade-off effect: thymol provides an increase in flexibility (EAB), yet at the same time diminishes the strength and stiffness. The best range of thymol for the balance of performance is 2-4%, at which the likelihood of meeting all three criteria is highest.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 .

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

