Influence of Ionic Size on the concentration of Ag+ and Zn2+ in Simulated Body Fluid: Modeling and Monte Carlo Simulation with Dental Applications
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.61882/jcc.6.4.5Abstract
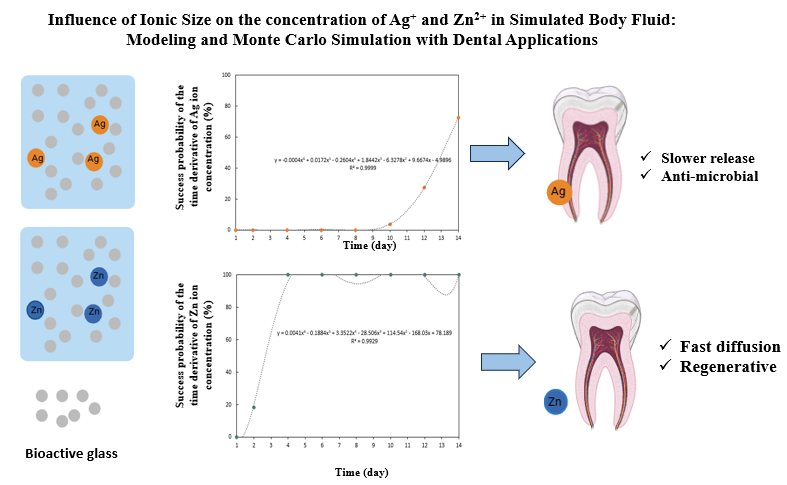
This study examines the impact of silver (Ag+) and zinc (Zn2+) ions on the behavior of bioactive glass for dental applications, utilizing computational modeling and Monte Carlo simulations. Bioactive glasses are increasingly incorporated into dental restorative materials, pulp capping agents, and implant coatings due to their ability to release therapeutic ions that promote antimicrobial activity and tissue regeneration. Ion concentration profiles in simulated body fluid were modeled over time to evaluate the differences in release behavior between Ag+ and Zn2+. The results indicate that Zn2+, due to its smaller ionic radius, demonstrates higher mobility and faster diffusion through the glass matrix, whereas Ag+ exhibits slower release kinetics and partial retention within the structure. Monte Carlo simulations captured the probabilistic nature of ion transport, offering insights into temporal variations and release efficiencies. These findings underscore the critical role of ionic size and transport dynamics in designing bioactive glasses with controlled ion release profiles. In the dental context, optimized Zn2+ and Ag+ delivery may enhance remineralization, pulpal healing, and long-term antimicrobial protection, supporting the development of advanced, bioactive dental materials.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 .

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

