Self-expanding stents based on shape memory alloys and shape memory polymers
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29252/jcc.2.2.5Keywords:
Self-expanding stents, Shape memory alloys, Shape memory polymers, NitinolAbstract
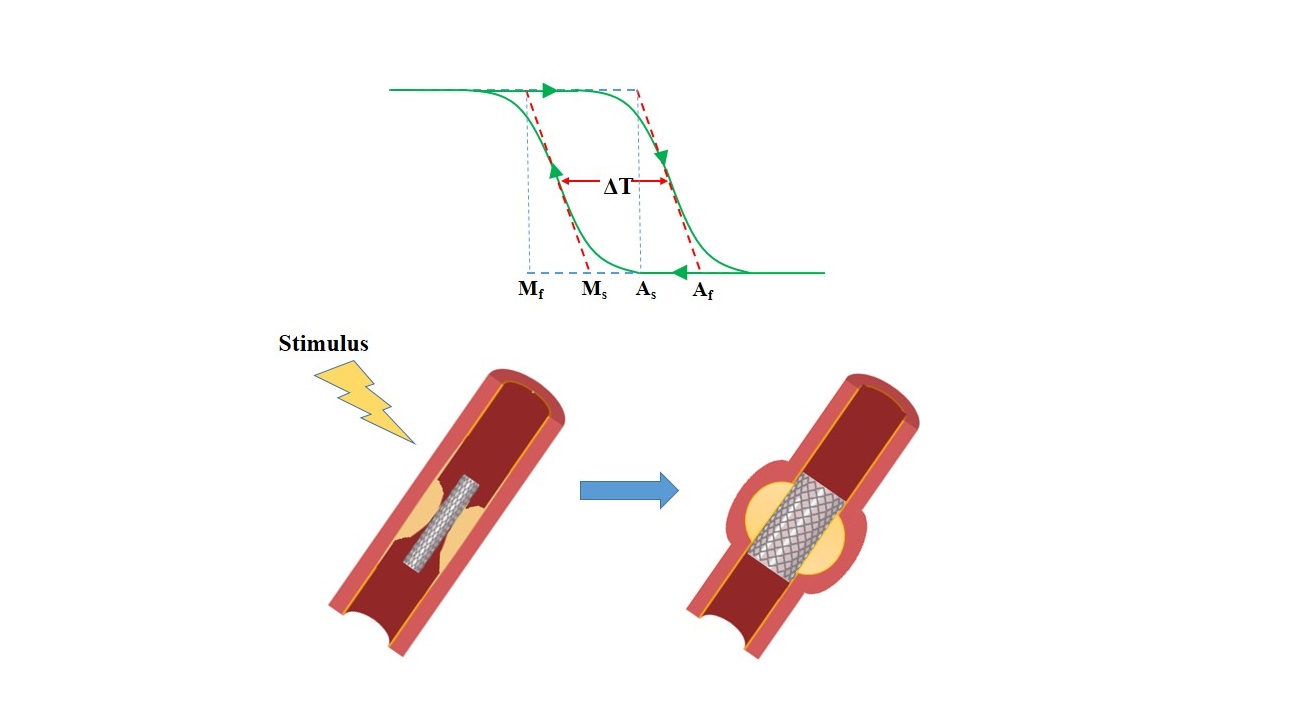
A stenotic vessel can be opened using net-shape tubes called “stents” leading to the restoration of the bloodstream. Compared to the commonly used stainless steel stent, self-expandable stents have some advantages. They do not suffer from the risks of damage to the vascular tissue due to the balloon expansion. Moreover, overexpansion for compensating the elastic recoil is not needed, and there is no constant force applied on the artery until the occlusion of the device by the artery stops. However, the stent cannot restore the original dimensions of the vessel in the case of calcified plaques. Self-expandable stents can be utilized for the treatment of atherosclerotic lesions in the carotid, coronary, and peripheral arteries. Shape memory alloys (SMAs), mainly NiTi (nitinol), are employed for self-expandable vascular stent applications. Nitinol is widely applied for medical devices and implants due to its excellent fatigue performance, mechanical properties, and biocompatibility, which make this alloy suitable for long-term installations. Other materials used for self-expandable cardiovascular stents are shape memory polymers (SMPs). Shape memory effect is triggered by the hydration of polymers or temperature change preventing the collapse of small blood vessels. This review has focused on the mechanisms and properties of SMAs and SMPs as promising materials for stent application.
References
W. Huang, Z. Ding, C. Wang, J. Wei, Y. Zhao, H. Purnawali, Shape memory materials, Materials today 13(7-8) (2010) 54-61.
A. Lendlein, R. Langer, Biodegradable, elastic shape-memory polymers for potential biomedical applications, Science 296(5573) (2002) 1673-1676.
H. Won Jang, A. Zareidoost, M. Moradi, A. Abuchenari, A. Bakhtiari, R. Pouri-amanesh, B. Malekpouri, A. Jafari Rad, Photosensitive nanocomposites: environ-mental and biological applications, Journal of Composites and Compounds 1(1) (2020).
L. Bazli, M.H. Bagherian, M. Karrabi, F. Abbassi?Sourki, H. Azizi, Effect of starch ratio and compatibilization on the viscoelastic behavior of POE/starch blends, Journal of Applied Polymer Science 137(29) (2020) 48877.
Q. Meng, J. Hu, A review of shape memory polymer composites and blends, Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing 40(11) (2009) 1661-1672.
T. Pretsch, Review on the functional determinants and durability of shape memory polymers, Polymers 2(3) (2010) 120-158.
L. Bazli, A. Khavandi, M.A. Boutorabi, M. Karrabi, Morphology and visco-elastic behavior of silicone rubber/EPDM/Cloisite 15A nanocomposites based on Maxwell model, Iranian Polymer Journal 25(11) (2016) 907-918.
J. Parameswaranpillai, S. Siengchin, J.J. George, S. Jose, Shape Memory Polymers, Blends and Composites: Advances and Applications, Springer Singa-pore2019.
M.C. Serrano, G.A. Ameer, Recent insights into the biomedical applications of shape?memory polymers, Macromolecular bioscience 12(9) (2012) 1156-1171.
L. Chang, T. Read, Plastic deformation and diffusionless phase changes in metals—The gold-cadmium beta phase, JOM 3(1) (1951) 47-52.
L.B. Vernon, H.M. Vernon, Process of manufacturing articles of thermoplastic synthetic resins, Google Patents, 1941.
W.J. Buehler, J. Gilfrich, R. Wiley, Effect of low?temperature phase changes on the mechanical properties of alloys near composition TiNi, Journal of applied physics 34(5) (1963) 1475-1477.
E. Sharifi Sedeh, S. Mirdamadi, F. Sharifianjazi, M. Tahriri, Synthesis and evaluation of mechanical and biological properties of scaffold prepared from Ti and Mg with different volume percent, Synthesis and Reactivity in Inorganic, Met-al-Organic, and Nano-Metal Chemistry 45(7) (2015) 1087-1091.
E. Asadi, A. Fassadi Chimeh, S. Hosseini, S. Rahimi, B. Sarkhosh, L. Bazli, R. Bashiri, A.H. Vakili Tahmorsati, A Review of Clinical Applications of Graphene Quantum Dot-based Composites, Composites and Compounds 1(1) (2019).
S. Nasibi, K. Alimohammadi, L. Bazli, S. Eskandarinezhad, A. Mohammadi, N. Sheysi, TZNT alloy for surgical implant applications: A Systematic Review, Composites and Compounds 2(2) (2020).
T. Duerig, D. Richter, J. Albrecht, Shape memory in Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al, Scripta Metallurgica 16(8) (1982) 957-961.
M. Swain, Shape memory behaviour in partially stabilized zirconia ceramics, Nature 322(6076) (1986) 234-236.
T.W. Duerig, J. Albrecht, G.H. Gessinger, A shape-memory alloy for high-tem-perature applications, JOM 34(12) (1982) 14-20.
W. Huang, On the selection of shape memory alloys for actuators, Materials
S. Omid et al. / Journal of Composites and Compounds 2 (2020) 92-9897& design 23(1) (2002) 11-19.
S. Ota, Current status of irradiated heat-shrinkable tubing in Japan, Radiation Physics and Chemistry (1977) 18(1-2) (1981) 81-87.
D. Ratna, J. Karger-Kocsis, Recent advances in shape memory polymers and composites: a review, Journal of Materials Science 43(1) (2008) 254-269.
J. Parameswaranpillai, S. Siengchin, Shape Memory Polymers, Applied Sci-ence and Engineering Progress 10(2) (2017).
T. Hirai, H. Maruyama, T. Suzuki, S. Hayashi, Shape memorizing properties of a hydrogel of poly (vinyl alcohol), Journal of applied polymer science 45(10) (1992) 1849-1855.
T. Hirai, H. Maruyama, T. Suzuki, S. Hayashi, Effect of chemical cross?link-ing under elongation on shape restoring of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel, Journal of applied polymer science 46(8) (1992) 1449-1451.
B.K. Kim, S.Y. Lee, M. Xu, Polyurethanes having shape memory effects, Polymer-Letchworth 37(26) (1996) 5781-5794.
F. Li, X. Zhang, J. Hou, M. Xu, X. Luo, D. Ma, B.K. Kim, Studies on thermal-ly stimulated shape memory effect of segmented polyurethanes, Journal of Applied Polymer Science 64(8) (1997) 1511-1516.
L. Lecce, A. Concilio, Shape Memory Alloy Engineering: For Aerospace, Structural and Biomedical Applications, Elsevier Science2014.
J. Parameswaranpillai, S.P. Ramanan, J.J. George, S. Jose, A.K. Zachariah, S. Siengchin, K. Yorseng, A. Janke, J.r. Pionteck, PEG-ran-PPG modified epoxy ther-mosets: a simple approach to develop tough shape memory polymers, Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 57(10) (2018) 3583-3590.
Y. Liu, K. Gall, M.L. Dunn, A.R. Greenberg, J. Diani, Thermomechanics of shape memory polymers: uniaxial experiments and constitutive modeling, Interna-tional Journal of Plasticity 22(2) (2006) 279-313.
J. Parameswaranpillai, S.P. Ramanan, S. Jose, S. Siengchin, A. Magueresse, A. Janke, J.r. Pionteck, Shape memory properties of Epoxy/PPO–PEO–PPO triblock copolymer blends with tunable thermal transitions and mechanical characteristics, Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 56(47) (2017) 14069-14077.
M. Behl, J. Zotzmann, A. Lendlein, Shape-memory polymers and shape-changing polymers, Shape-Memory Polymers, Springer2009, pp. 1-40.
E. Oliver, T. Mori, M. Daymond, P. Withers, Neutron diffraction study of stress-induced martensitic transformation and variant change in Fe–Pd, Acta mate-rialia 51(20) (2003) 6453-6464.
E. Gautier, E. Patoor, Experimental observations for shape memory alloys and transformation induced plasticity phenomena, Mechanics of Solids with Phase Changes, Springer1997, pp. 69-103.
E. Patoor, D.C. Lagoudas, P.B. Entchev, L.C. Brinson, X. Gao, Shape memory alloys, Part I: General properties and modeling of single crystals, Mechanics of materials 38(5-6) (2006) 391-429.
C. WYAMAN, Shape memory and related phenomena, Progress in materials Science 36 (1992) 203-224.
D. Mantovani, Shape memory alloys: Properties and biomedical applications, Jom 52(10) (2000) 36-44.
S.A. Shabalovskaya, Surface, corrosion and biocompatibility aspects of Ni-tinol as an implant material, Bio-medical materials and engineering 12(1) (2002) 69-109.
S.W. Bokhari, O. Vahdat, R.J. Winters, The first clinical experience with a peripheral, self-expanding nitinol stent in the treatment of saphenous vein graft disease: angiographic evidence of late expansion, The Journal of invasive cardiol-ogy 15(7) (2003) 418-422.
D. Stoeckel, A. Pelton, T. Duerig, Self-expanding nitinol stents: material and design considerations, European radiology 14(2) (2004) 292-301.
A. Bezrouk, J. Hanus, J. Záhora, Temperature characteristics of nitinol spiral stents, Scripta Med (Brno) 78 (2005) 219-226.
M. Mikulewicz, K. Chojnacka, Release of metal ions from orthodontic appli-ances by in vitro studies: a systematic literature review, Biological trace element research 139(3) (2011) 241-256.
M. Es-Souni, M. Es-Souni, H. Fischer-Brandies, Assessing the biocompati-bility of NiTi shape memory alloys used for medical applications, Analytical and bioanalytical chemistry 381(3) (2005) 557-567.
A.M. Barcelos, A.S. Luna, N.d.A. Ferreira, A.V.C. Braga, D.C.B.d. Lago, L.F.d. Senna, Corrosion evaluation of orthodontic wires in artificial saliva solu-tions by using response surface methodology, Materials Research 16(1) (2013) 50-64.
S. Shabalovskaya, J. Anderegg, J. Van Humbeeck, Critical overview of Niti-nol surfaces and their modifications for medical applications, Acta biomaterialia 4(3) (2008) 447-467.
S. Robertson, A. Pelton, R. Ritchie, Mechanical fatigue and fracture of Niti-nol, International Materials Reviews 57(1) (2012) 1-37.
A. Pelton, Nitinol fatigue: a review of microstructures and mechanisms, Jour-nal of Materials Engineering and Performance 20(4-5) (2011) 613-617.
Y. Shen, W. Qian, H. Abtin, Y. Gao, M. Haapasalo, Fatigue testing of con-trolled memory wire nickel-titanium rotary instruments, Journal of endodontics 37(7) (2011) 997-1001.
A. Pelton, J. Fino-Decker, L. Vien, C. Bonsignore, P. Saffari, M. Launey, M. Mitchell, Rotary-bending fatigue characteristics of medical-grade Nitinol wire, Journal of the mechanical behavior of biomedical materials 27 (2013) 19-32.
F. Mohammadi, N. Golafshan, M. Kharaziha, A. Ashrafi, Chitosan-heparin nanoparticle coating on anodized NiTi for improvement of blood compatibility and biocompatibility, Int J Biol Macromol 127 (2019) 159-168.
A.I. Lotkov, O.A. Kashin, A.N. Kudryashov, K.V. Krukovsky, Structure and properties of self-expanding intravascular NiTi stents doped with Si ions, Materi-als Today: Proceedings 4(3) (2017) 4647-4651.
C. Park, S. Kim, H.-E. Kim, T.-S. Jang, Mechanically stable tantalum coating on a nano-roughened NiTi stent for enhanced radiopacity and biocompatibility, Surface and Coatings Technology 305 (2016) 139-145.
D. Yang, X. Lu, Y. Hong, T. Xi, D. Zhang, The molecular mechanism for ef-fects of TiN coating on NiTi alloy on endothelial cell function, Biomaterials 35(24) (2014) 6195-205.
J. Witkowska, A. Sowinska, E. Czarnowska, T. Plocinski, B. Rajchel, M. Tar-nowski, T. Wierzchon, Structure and properties of composite surface layers pro-duced on NiTi shape memory alloy by a hybrid method, J Mater Sci Mater Med 29(8) (2018) 110.
R. Bakhshi, A. Darbyshire, J.E. Evans, Z. You, J. Lu, A.M. Seifalian, Poly-meric coating of surface modified nitinol stent with POSS-nanocomposite poly-mer, Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 86(1) (2011) 93-105.
C.M. Yakacki, R. Shandas, C. Lanning, B. Rech, A. Eckstein, K. Gall, Uncon-strained recovery characterization of shape-memory polymer networks for cardio-vascular applications, Biomaterials 28(14) (2007) 2255-63.
G.M. Baer, T.S. Wilson, W. Small IV, J. Hartman, W.J. Benett, D.L. Matthews, D.J. Maitland, Thermomechanical properties, collapse pressure, and expansion of shape memory polymer neurovascular stent prototypes, Journal of Biomedical Ma-terials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials 90(1) (2009) 421-429.
H. Wache, D. Tartakowska, A. Hentrich, M. Wagner, Development of a poly-mer stent with shape memory effect as a drug delivery system, Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 14(2) (2003) 109-112.
P.W. Serruys, M.J. Kutryk, A.T. Ong, Coronary-artery stents, New England Journal of Medicine 354(5) (2006) 483-495.
J.C. Palmaz, Intravascular stents in the last and the next 10 years, Journal of endovascular therapy 11(6_suppl) (2004) II-200-II-206.
T. Hu, C. Yang, S. Lin, Q. Yu, G. Wang, Biodegradable stents for coronary ar-tery disease treatment: Recent advances and future perspectives, Materials Science and Engineering: C 91 (2018) 163-178.
J. Daraei, Production and characterization of PCL (Polycaprolactone) coated TCP/nanoBG composite scaffolds by sponge foam method for orthopedic applica-tions, Journal of Composites and Compounds 1(1) (2020).
H. Tamai, K. Igaki, E. Kyo, K. Kosuga, A. Kawashima, S. Matsui, H. Komori, T. Tsuji, S. Motohara, H. Uehata, Initial and 6-month results of biodegradable poly-l-lactic acid coronary stents in humans, Circulation 102(4) (2000) 399-404.
S.S. Venkatraman, L.P. Tan, J.F.D. Joso, Y.C.F. Boey, X. Wang, Biodegradable stents with elastic memory, Biomaterials 27(8) (2006) 1573-1578.
M. Radmansouri, E. Bahmani, E. Sarikhani, K. Rahmani, F. Sharifianjazi, M. Irani, Doxorubicin hydrochloride-Loaded electrospun chitosan/cobalt ferrite/tita-nium oxide nanofibers for hyperthermic tumor cell treatment and controlled drug release, International journal of biological macromolecules 116 (2018) 378-384.
P. Abasian, M. Radmansouri, M.H. Jouybari, M.V. Ghasemi, A. Mohammadi, M. Irani, F.S. Jazi, Incorporation of magnetic NaX zeolite/DOX into the PLA/chi-tosan nanofibers for sustained release of doxorubicin against carcinoma cells death in vitro, International journal of biological macromolecules 121 (2019) 398-406.
A. Kraitzer, Y. Kloog, M. Zilberman, Approaches for prevention of resteno-sis, Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials: An Official Journal of The Society for Biomaterials, The Japanese Society for Bio-materials, and The Australian Society for Biomaterials and the Korean Society for Biomaterials 85(2) (2008) 583-603.
H.S. Jang, H.Y. Nam, J.M. Kim, D.H. Hahm, S.H. Nam, K.L. Kim, J.R. Joo, W. Suh, J.S. Park, D.K. Kim, Effects of curcumin for preventing restenosis in a hypercholesterolemic rabbit iliac artery stent model, Catheterization and Cardio-vascular Interventions 74(6) (2009) 881-888.
G. Nakazawa, A.V. Finn, F.D. Kolodgie, R. Virmani, A review of current de-vices and a look at new technology: drug-eluting stents, Expert review of medical devices 6(1) (2009) 33-42.
A. Biswas, A.P. Singh, D. Rana, V.K. Aswal, P. Maiti, Biodegradable tough-ened nanohybrid shape memory polymer for smart biomedical applications, Na-noscale 10(21) (2018) 9917-9934.
W. Small, P.R. Buckley, T.S. Wilson, W.J. Benett, J. Hartman, D. Saloner, D.J. Maitland, Shape memory polymer stent with expandable foam: a new concept for endovascular embolization of fusiform aneurysms, IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 54(6 Pt 2) (2007) 1157-60.
L. Sun, W.M. Huang, Thermo/moisture responsive shape-memory polymer for possible surgery/operation inside living cells in future, Materials & Design (1980-2015) 31(5) (2010) 2684-2689.
L. Xue, S. Dai, Z. Li, Biodegradable shape-memory block co-polymers for fast self-expandable stents, Biomaterials 31(32) (2010) 8132-40.
G.M. Baer, T.S. Wilson, W.t. Small, J. Hartman, W.J. Benett, D.L. Matthews, D.J. Maitland, Thermomechanical properties, collapse pressure, and expansion of shape memory polymer neurovascular stent prototypes, J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 90(1) (2009) 421-9.
R. Liu, S. McGinty, F. Cui, X. Luo, Z. Liu, Modelling and simulation of the expansion of a shape memory polymer stent, Engineering Computations 36(8) (2019) 2726-2746.
M. Ansari, M. Golzar, M. Baghani, M. Soleimani, Shape memory characteri-zation of poly(?-caprolactone) (PCL)/polyurethane (PU) in combined torsion-ten-sion loading with potential applications in cardiovascular stent, Polymer Testing 68 (2018) 424-432.
H. Jia, S.-Y. Gu, K. Chang, 3D printed self-expandable vascular stents from biodegradable shape memory polymer, Advances in Polymer Technology 37(8) (2018) 3222-3228.
C. Lin, L. Zhang, Y. Liu, L. Liu, J. Leng, 4D printing of personalized shape memory polymer vascular stents with negative Poisson’s ratio structure: A prelimi-nary study, Science China Technological Sciences 63(4) (2020) 578-588.
Article DOR: 20.1001.1.26765837.2020.2.3.5.5
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2020 JCC Research Group

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

